OverTheWire: Bandit学习笔记-Level 6-10
本文的通关方法并不是唯一的最好的方法,仅供参考。
参考书籍:
Bandit Level 6
Level Goal
The password for the next level is stored somewhere on the server and has all of the following properties:
owned by user bandit7
owned by group bandit6
33 bytes in size
Commands you may need to solve this level
按照提示,使用find命令,
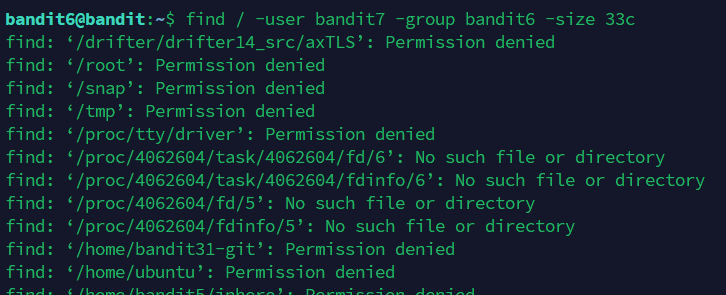

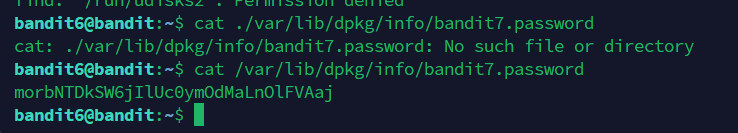
得密码:morbNTDkSW6jIlUc0ymOdMaLnOlFVAaj
ls , cd , cat , file , du , find , grepBandit Level 7
The password for the next level is stored in the file data.txt next to the word millionth按照提示,使用grep这个命令可以匹配文件中的字符,

grep (global search regular expression(RE) and print out the line,全面搜索正则表达式并把行打印出来)是一种强大的文本搜索工具,它能使用正则表达式搜索文本,并把匹配的行打印出来。用于过滤/搜索的特定字符。可使用正则表达式能配合多种命令使用,使用上十分灵活。
得密码:dfwvzFQi4mU0wfNbFOe9RoWskMLg7eEc
andit Level 8
The password for the next level is stored in the file data.txt and is the only line of text that occurs only once按照提示,使用uniq这个命令可以匹配文件中的字符,uniq要跟sort一起用,因为uniq是通过比较上下行字符串来判断是否重复,所以先sort再uniq,

得密码:4CKMh1JI91bUIZZPXDqGanal4xvAg0JM
知识点补充uniq命令 显示或忽略重复的行。
uniq语法:
uniq [OPTION]... [INPUT [OUTPUT]]选项
-c, --count 在每行开头增加重复次数。
-d, --repeated 所有邻近的重复行只被打印一次。
-D 所有邻近的重复行将全部打印。
--all-repeated[=METHOD] 类似于 -D,但允许每组之间以空行分割。METHOD取值范围{none(默认),prepend,separate}。
-f, --skip-fields=N 跳过对前N个列的比较。
--group[=METHOD] 显示所有行,允许每组之间以空行分割。METHOD取值范围:{separate(默认),prepend,append,both}。
-i, --ignore-case 忽略大小写的差异。
-s, --skip-chars=N 跳过对前N个字符的比较。
-u, --unique 只打印非邻近的重复行。
-z, --zero-terminated 设置行终止符为NUL(空),而不是换行符。
-w, --check-chars=N 只对每行前N个字符进行比较。
--help 显示帮助信息并退出。
--version 显示版本信息并退出。知识点补充sort命令 对文本文件中所有行进行排序。
file语法:
sort [OPTION]... [FILE]...
sort [OPTION]... --files0-from=F选项
-b, --ignore-leading-blanks 忽略开头的空白。
-d, --dictionary-order 仅考虑空白、字母、数字。
-f, --ignore-case 将小写字母作为大写字母考虑。
-g, --general-numeric-sort 根据数字排序。
-i, --ignore-nonprinting 排除不可打印字符。
-M, --month-sort 按照非月份、一月、十二月的顺序排序。
-h, --human-numeric-sort 根据存储容量排序(注意使用大写字母,例如:2K 1G)。
-n, --numeric-sort 根据数字排序。
-R, --random-sort 随机排序,但分组相同的行。
--random-source=FILE 从FILE中获取随机长度的字节。
-r, --reverse 将结果倒序排列。
--sort=WORD 根据WORD排序,其中: general-numeric 等价于 -g,human-numeric 等价于 -h,month 等价于 -M,numeric 等价于 -n,random 等价于 -R,version 等价于 -V。
-V, --version-sort 文本中(版本)数字的自然排序。andit Level 9
The password for the next level is stored in the file data.txt in one of the few human-readable strings, preceded by several ‘=’ characters.按照提示使用strings命令,在对象文件或二进制文件中查找可打印的字符串。字符串是4个或更多可打印字符的任意序列,以换行符或空字符结束。 strings命令对识别随机对象文件很有用。
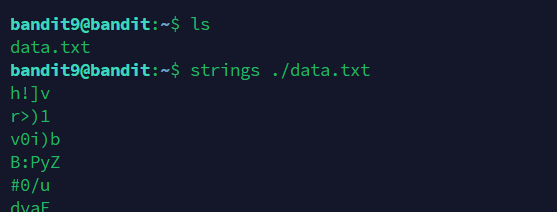
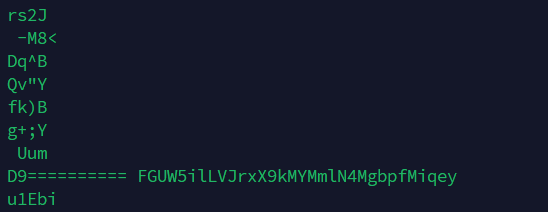
得密码:FGUW5ilLVJrxX9kMYMmlN4MgbpfMiqey
知识点补充strings命令 在对象文件或二进制文件中查找可打印的字符串。
file语法:
strings [ -a ] [ - ] [ -o ] [ -t Format ] [ -n Number ] [ -Number ] [file ... ]选项
-a --all:扫描整个文件而不是只扫描目标文件初始化和装载段
-f –print-file-name:在显示字符串前先显示文件名
-n –bytes=[number]:找到并且输出所有NUL终止符序列
- :设置显示的最少的字符数,默认是4个字符
-t --radix={o,d,x} :输出字符的位置,基于八进制,十进制或者十六进制
-o :类似--radix=o
-T --target= :指定二进制文件格式
-e --encoding={s,S,b,l,B,L} :选择字符大小和排列顺序:s = 7-bit, S = 8-bit, {b,l} = 16-bit, {B,L} = 32-bit
@ :读取中选项andit Level 10
The password for the next level is stored in the file data.txt, which contains base64 encoded data
得秘密:The password is dtR173fZKb0RRsDFSGsg2RWnpNVj3qRr
本文是原创文章,采用 CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 协议,完整转载请注明来自 loekr
评论
匿名评论
隐私政策
你无需删除空行,直接评论以获取最佳展示效果
Steam卡片

